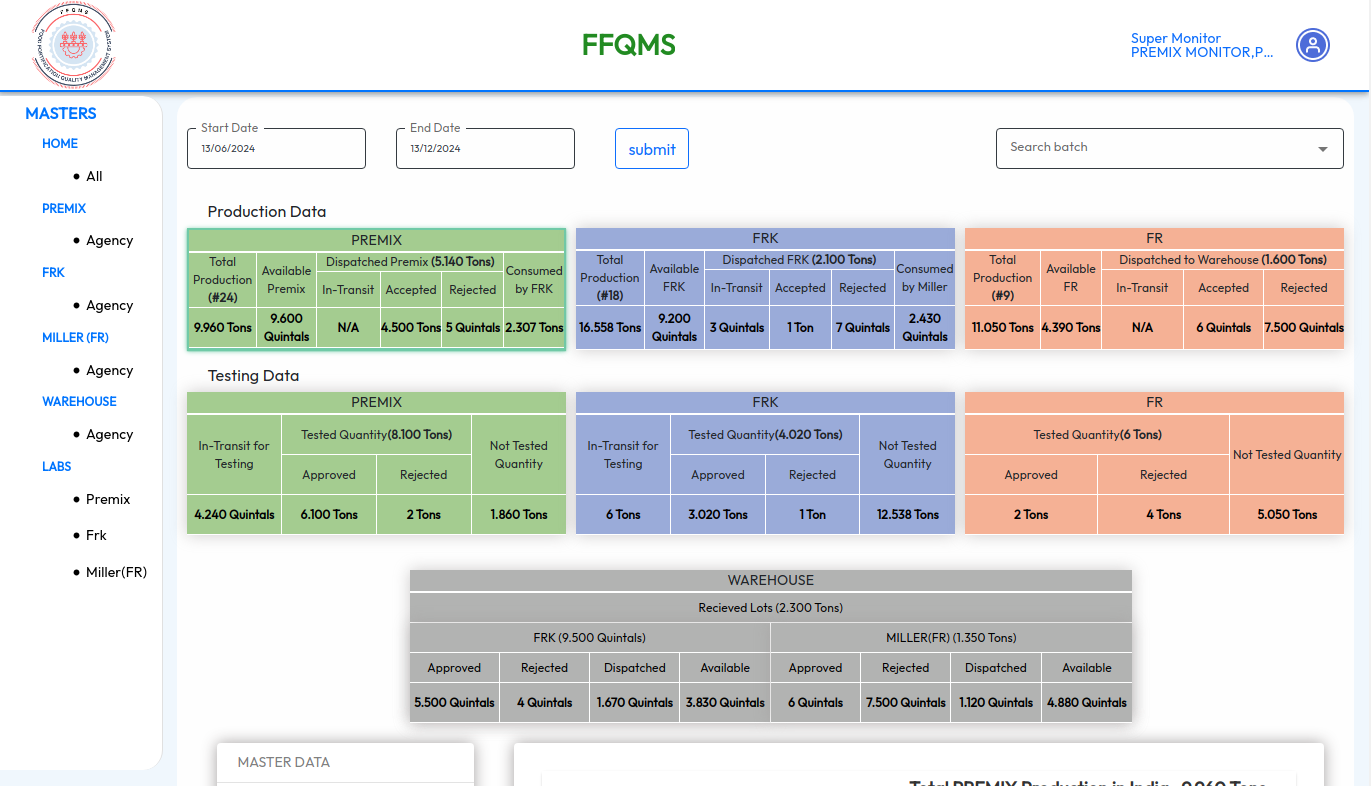
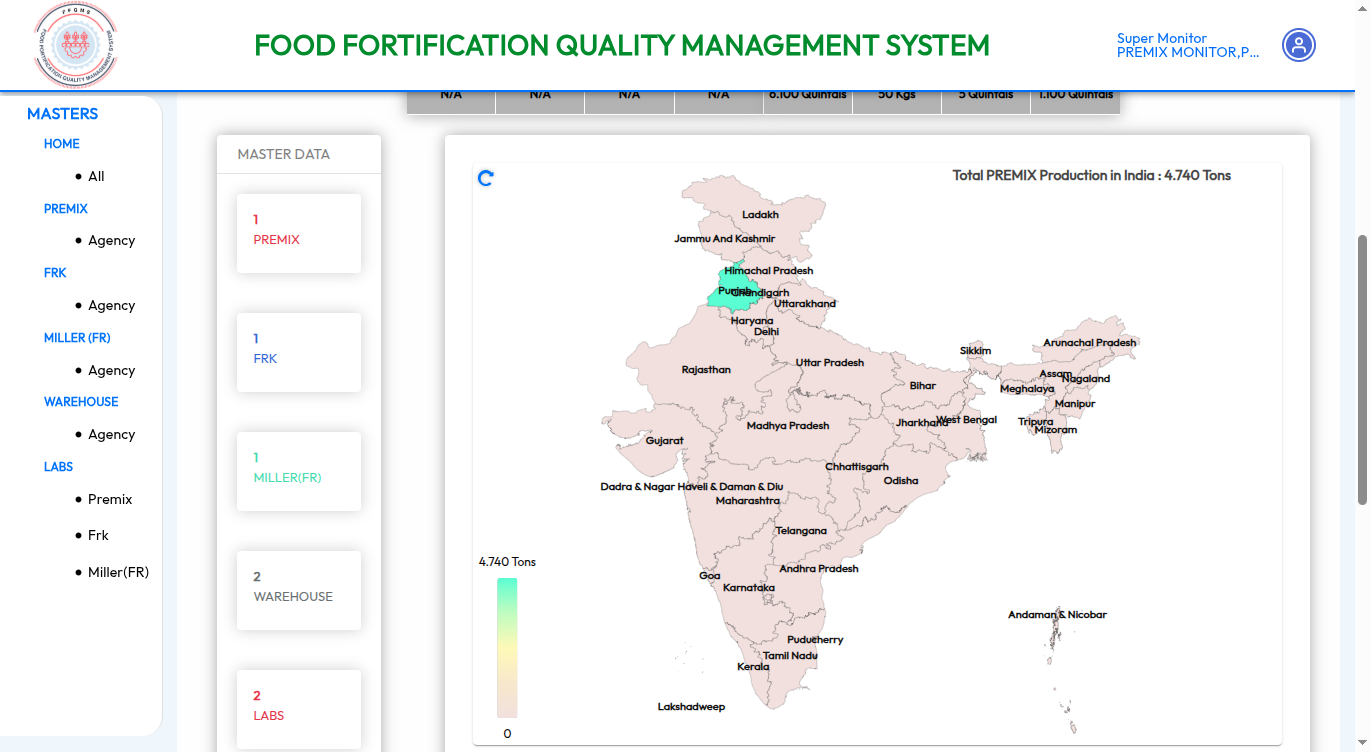
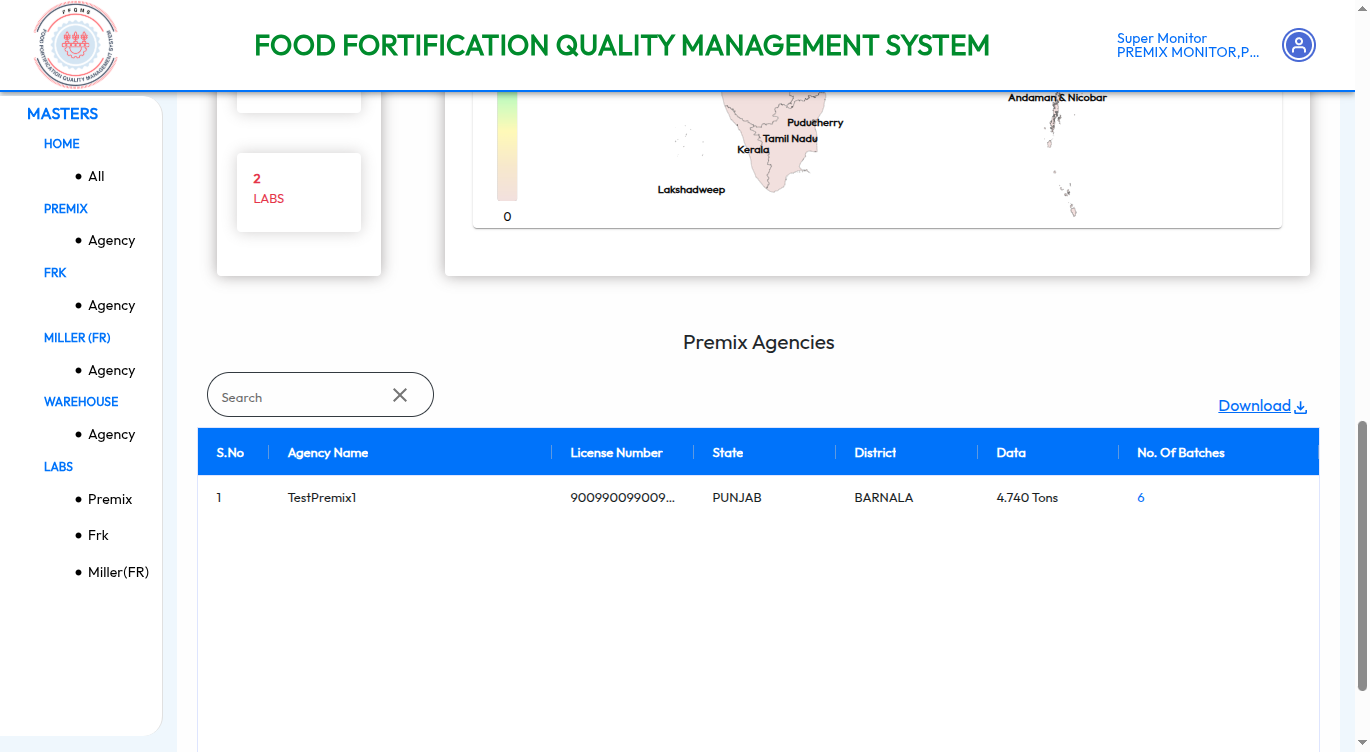
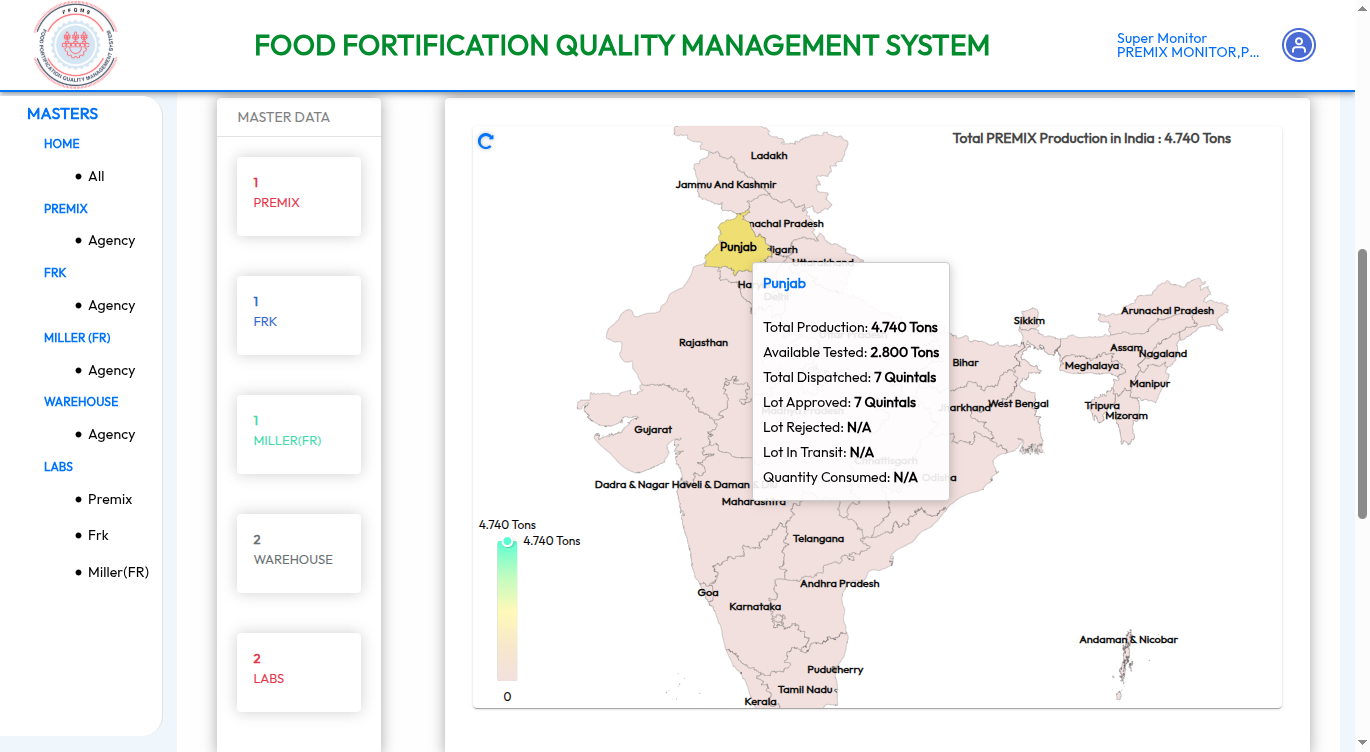
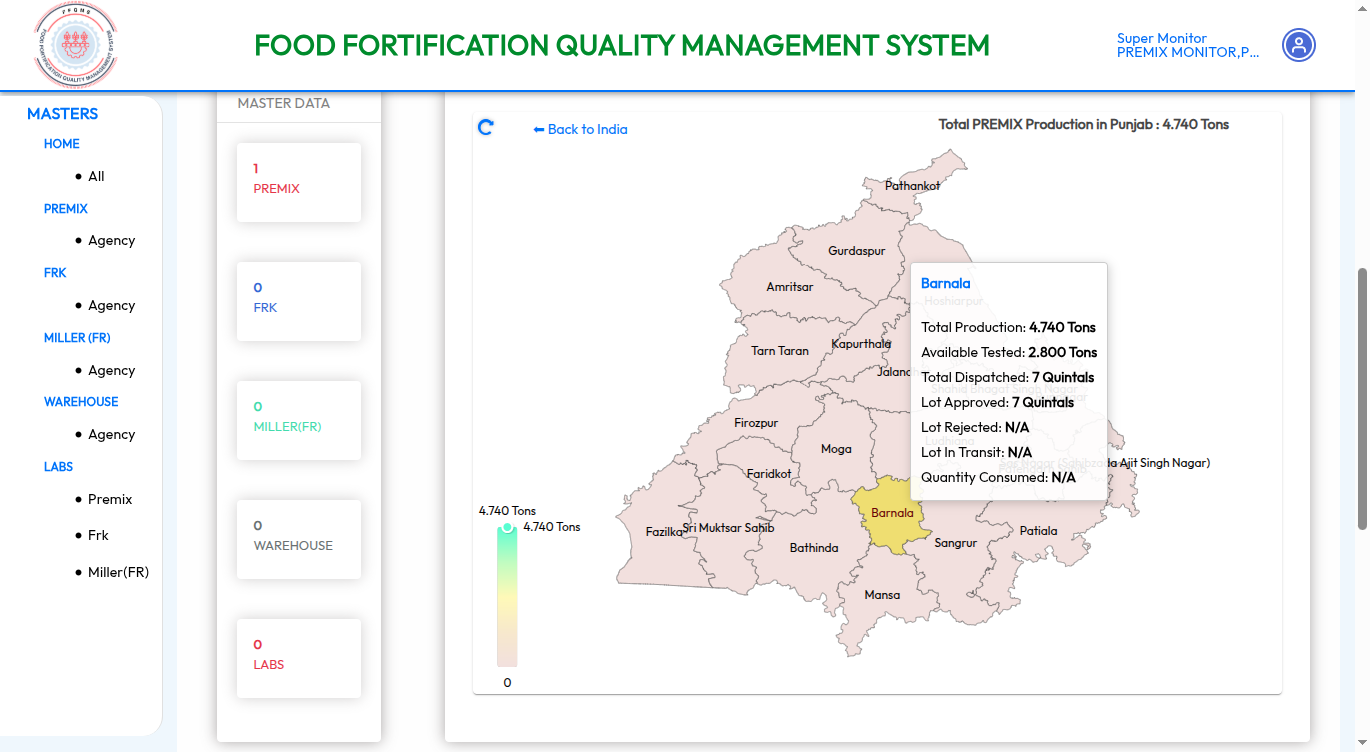
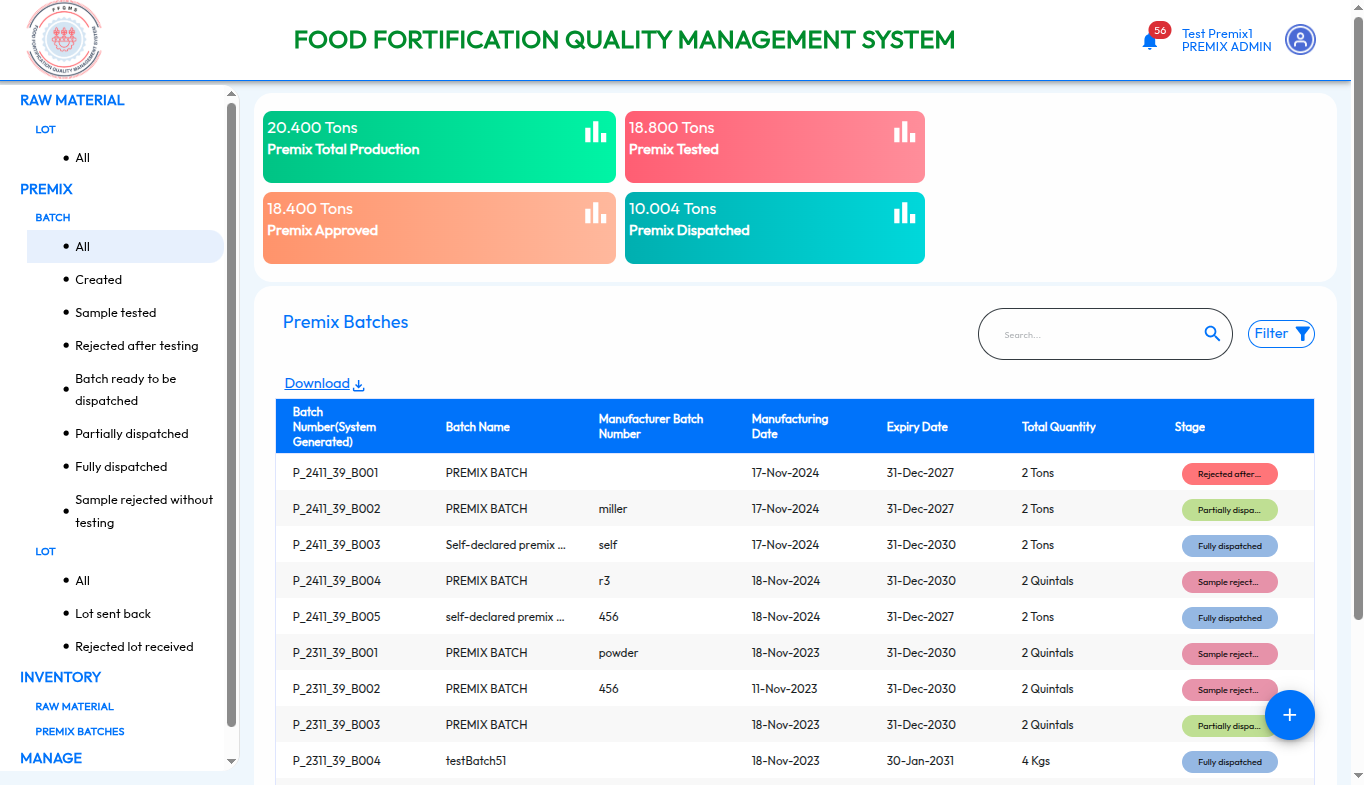
Food Fortification Quality Management System
The Food Fortification Quality Management System (FFQMS) is a digital platform designed to ensure the quality and traceability of fortified food products. It integrates various modules to support comprehensive quality control (QC), quality assurance (QA), traceability, and compliance with industry and government regulations. It is built with scalability and configurability in mind, allowing the system to adapt to different commodities and regional standards. The application is customizable for any commodity; currently, FFQMS has been developed using rice as the primary use case.